O que é Espaço e Tempo (SXT)?
Introdução
Os últimos anos têm visto um rápido crescimento da indústria blockchain. No entanto, a tecnologia inovadora ainda enfrenta problemas de acesso e processamento de grandes conjuntos de dados necessários para criar plataformas como protocolos de empréstimo que oferecem taxas de empréstimo de acordo com a pontuação de crédito do usuário.
Para resolver este problema, o Space and Time (SXT) foi desenvolvido para mudar a forma como as empresas, usuários e desenvolvedores lidam, transportam e armazenam dados, oferecendo utilidade e facilitando o desenvolvimento.
O que é Espaço e Tempo?

Fonte: Site Oficial
Space and Time é uma plataforma projetada para fornecer contratos inteligentes com processamento de dados descentralizado, permitindo que eles processem dados em diferentes nós em vez de uma única autoridade central.
Ele consegue isso por meio de sua arquitetura de modelo que envolve escalonamentoprovas de conhecimento zero (ZK-Proofs)em um armazém descentralizado, distribuindo dados para diferentes nós em vez de um local central.
Isso permite que os desenvolvedores construam aplicativos orientados a dados em um ambiente completamente confiável, com acesso a dados abrangentes de blockchain coletados de várias outras cadeias.
A plataforma desenvolveu a Prova de SQL, uma prova ZK inovadora como um coprocessador ZK sub-segundo. Isso permite que o contrato inteligente questione sua cadeia e outras cadeias sobre determinadas transações e receba respostas comprovadas por ZK no próximo bloco.
Space and Time (SXT) introduz os usuários a um novo mundo de contratos inteligentes que combinam dados on-chain e off-chain para oferecer aos usuários uma economia mais robusta e aplicativos on-chain aprimorados com mais possibilidades.
História do Espaço e do Tempo
Espaço e Tempofoi co-fundada em 2022por Nate Holiday, Scott Dykstra, Jay White, e Craig Holiday. Desde o seu lançamento, passou por três estágios de financiamento, levantando mais de $50 milhões de investidores de alto nível, como Framework Ventures, Facção da Velocidade da Luz, Arrington Capital, e Capital do Hivemind.
Como Funcionam o Espaço e o Tempo?

Fonte: documentos
Space and Time são criados com uma arquitetura de dupla camada que compreende a Camada de Validador e um Armazém de Dados. Essas camadas trabalham em conjunto para garantir consultas fáceis e seguras contra dados on-chain e off-chain. O Validador ajuda a habilitar a comunicação entre redes de bancos de dados e clusters de computadores no armazém de dados do banco de dados.
O operador do nó do banco de dados é responsável por cada cluster de rede, controlando-os sem permissão enquanto controla a conectividade, disponibilidade e usabilidade do cluster do banco de dados. O validador, por outro lado, gerencia, comanda e verifica as tarefas realizadas por esses clusters, controlando o fluxo de dados e consultas entre os usuários finais e os clusters do armazém de dados.
Enquanto essas duas camadas trabalham juntas para garantir o sucesso da plataforma, elas realizam tarefas distintas dentro de cada camada.

Fonte: Site Oficial
Data Warehouse
O Data Warehouse serve como a espinha dorsal da plataforma Space and Time. Ele opera em um mecanismo de processamento híbrido transacional/analtico (HTAP) descentralizado e nativo da Web3, possibilitando desempenho confiável, escalável e eficiente para vários conjuntos de dados. Ele consiste em mltiplos clusters de rede que o operador gerencia de forma sem permissão.
Esses clusters executam cinco tarefas principais nos dados da plataforma:
- Ingestão de Dados: Os clusters são responsáveis por salvar dados obtidos fora da cadeia de blocos de redes e blockchains populares.
- Transporte de dados: Isso envolve transportar dados de um para outro.
- Armazenamento de Dados: Isso envolve salvar dados no depósito a partir de qualquer ponto no tempo.
- Transformação de Dados: Aqui, os clusters de rede participam da limpeza de dados, agregações de dados e junções de dados de várias fontes.
- Serviço de Dados: Os clusters de rede garantem acesso fácil e funcional aos dados, armazenamento inteligente em cache e a criação de APIs de dados.
Essas tarefas são possíveis por meio do processamento híbrido transacional/analítico (HTAP), que garante um bom gerenciamento de carga de trabalho por meio de um sistema que se adapta para executar qualquer carga de trabalho que lhe seja atribuída para processamento. Este é um motor perfeito para Espaço e Tempo, pois permite que os nós do armazém lidem com a ingestão de dados em alta velocidade e a agregação de dados em grande escala de mais de um terabyte de forma eficiente.
Validador
Isso pode ser referido como o sistema nervoso central do protocolo Espaço e Tempo, oferecendo diferentes microsserviços para garantir que a plataforma funcione sem problemas. Os papéis do Validador são divididos da seguinte forma:
- Roteamento: O roteamento é responsável por vincular transações e consultas com redes de armazenamento descentralizadas e vincular usuários aos seus dados. Os usuários interagem com o sistema como se estivesse conectado a um único cluster de rede sempre disponível. As solicitações são automaticamente direcionadas para a instância adequada do armazém de dados, lidando efetivamente com a distribuição de dados e quaisquer falhas potenciais em segundo plano.
- Streaming: O streaming assume o controle de cargas de trabalho de alto volume orientadas por eventos através Kafkapor sua durabilidade e tolerância a falhas. Com isso, os dados do usuário podem fluir para a rede e serem facilmente mesclados com os dados já armazenados.
- Consensus: O Consenso emprega a tolerância a falhas bizantinas para manter a integridade dos dados para as informações que entram e saem da plataforma. Os dados são submetidos à plataforma pelos processos TL Redundantes, e os Validadores então chegam a um acordo para produzir uma única saída. Através do Consenso, a plataforma protege dados críticos de erros ou atividades maliciosas, garantindo que sua integridade permaneça intacta.
- Prova de Consulta: A plataforma garante consultas SQL à prova de violação por meio da Prova de Consulta. Uma vez que os dados são inseridos, a prova de consulta gera uma impressão digital digital (hash). Quando um usuário solicita uma consulta segura, o banco de dados calcula os resultados e gera uma prova criptográfica. Esta prova é então enviada de volta para o banco de dados, onde é verificada em relação à impressão digital digital por meio da Prova de SQL da SxT.
Além disso, a Prova de Consulta funciona perfeitamente com o Consenso, fornecendo provas verificadas de forma redundante ao sistema de Consenso. Esse mecanismo ajuda a proteger contra ações maliciosas por verificadores e garante que a execução da consulta permaneça à prova de violações do início ao fim.
- Ancoragem de Tabela: A Ancoragem de Tabela garante a prova de armazenamento na plataforma ancorando tabelas on-chain. Atualiza uma árvore de Merkle toda vez que dados são adicionados à plataforma. Isso permite que validadores auditem clusters de armazéns de dados sem transmitir grandes volumes de dados.
Através do Table Anchoring, a plataforma pode realizar auditorias cíclicas. Isso é possível porque os hashes raiz são ancorados à cadeia através de smart contracts para acionar eventos, permitindo que a plataforma Space and Time verifique dados com segurança.
Recursos do Espaço e do Tempo
Junto com sua arquitetura complexa e multi-camadas, Space and Time também inclui várias características para garantir os melhores serviços para seus usuários. Algumas dessas características incluem:
Prova de SQL (Novel Sub-segundo ZK)
A plataforma também utiliza SQL, a linguagem de consulta de dados mais popular, para garantir uma experiência de construção amigável para desenvolvedores que constroem aplicações focadas em dados. Isso, por sua vez, torna a plataforma capaz de lidar com tarefas de processamento de dados mais complexas, não apenas recuperações de dados simples.
Dois papéis principais são desempenhados com a Prova de SQL: o cliente envia a consulta (Verificador) e o serviço de banco de dados calcula o resultado (Provador). Enquanto o Verificador normalmente envia uma consulta, ele também pode enviar uma entidade confiável, como um contrato inteligente. Isso funciona perfeitamente para aplicativos com armazenamento limitado que também precisam garantir que a análise de dados seja feita corretamente, sem que os dados sejam adulterados.
O Verificador e o Provador interagem entre si de duas maneiras distintas: Ingestão de Dados e Solicitação de Consulta. Com a Ingestão de Dados, o processo envolve um cliente enviando dados para inclusão no banco de dados. Os dados são enviados ao verificador, que gera um compromisso com informações suficientes para evitar a adulteração de informações em torno do protocolo.

Origem: documentos
Uma vez concluído este processo, o Verificador encaminha os dados para o armazenamento no banco de dados, mantendo o compromisso para uso futuro.
A segunda maneira como interagem é por meio de solicitações de consulta, que ocorrem quando o Verificador busca análises de dados sobre os dados armazenados pelo Provador. O serviço, cliente ou verificador inicia uma solicitação de consulta enviada ao Provador, que analisa a consulta, compila os resultados e gera uma prova juntamente com os resultados do verificador, mantendo o compromisso. O verificador, por meio da prova e do compromisso, agora pode verificar o resultado do Provador em relação à solicitação de consulta.

Fonte: documentos
SXT Chain
A cadeia SXT é um blockchain de dados comprovado por ZK para desenvolvedores, operadores de nós, investidores ou membros da comunidade. É uma testnet que permite aos usuários expandir os limites do que podem construir, fornecer feedback útil e ajudar a aprimorar a plataforma para melhorar seus serviços, tornando-a mais confiável e acelerando o lançamento de sua mainnet.
Armazém de Dados Descentralizado
A espinha dorsal da plataforma Space and Time é seu armazém de dados, que utiliza uma rede de nós distribuídos para garantir que os dados enviados sejam confiáveis e não estejam disponíveis em nenhum outro lugar na plataforma.
Índice de Blockchain
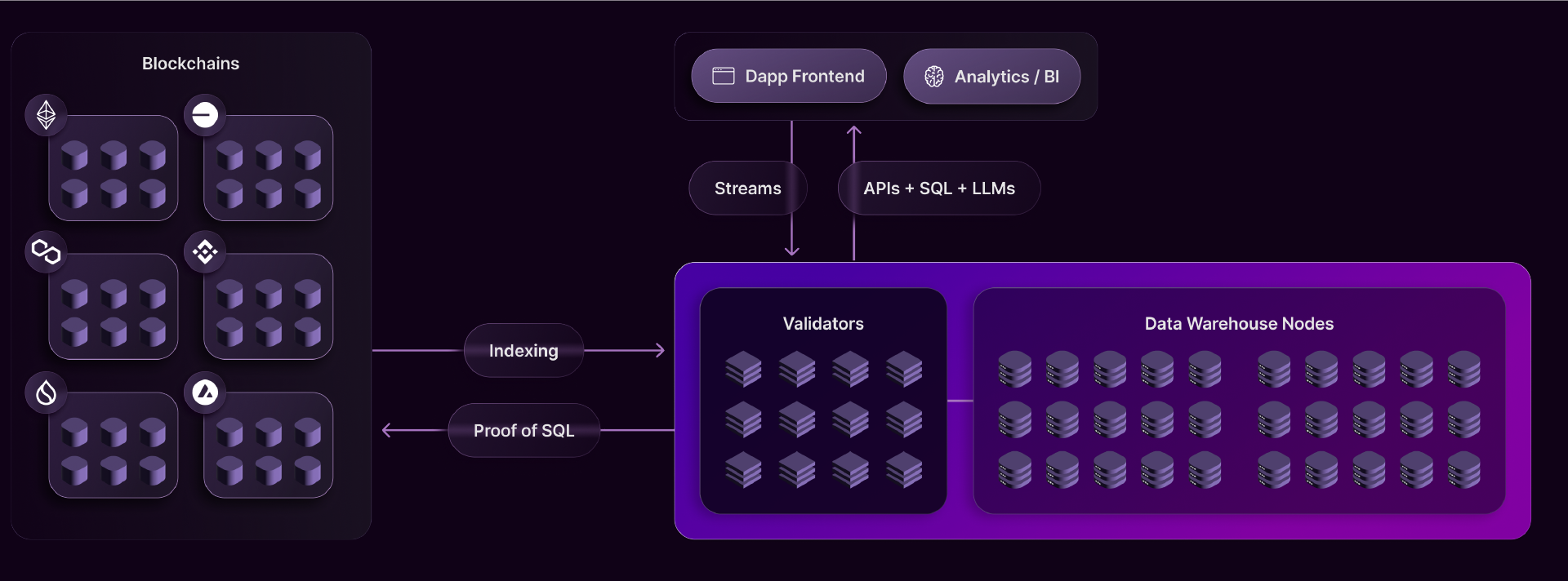
Origem: documentos
A natureza descentralizada dos dados da blockchain significa que os dados são distribuídos entre diferentes nós sem uma maneira integrada de consultar esses dados. Space and Time resolve esse problema lendo os dados de todas as blockchains, decodificando-os e escrevendo-os em tabelas de banco de dados relacionais.
Esse processo começa com a consulta individual dos nós de arquivo da blockchain com chamadas RPC para obter dados da blockchain em tempo real e históricos. A plataforma extrai dados da blockchain finalizada ao sondar continuamente blocos em tempo real dos nós da blockchain, recuperando blocos anteriores para construir um registro histórico completo e, por último, decodificando os dados atuais do contrato em uma nova tabela.
O próximo passo é o consenso. Aqui, a rede valida os dados da blockchain, eliminando a necessidade de um intermediário. Uma vez validados, os dados processados são enviados para o depósito de dados, onde podem ser facilmente consultados.
Dados de Blockchain Verificados

Origem: Site Oficial
A plataforma Space and Time oferece APIs web3 pré-construídas para desenvolvedores, concedendo-lhes acesso a centenas de dados em tempo real indexados derivados de grandes redes como Ethereum,ZKsync, Bitcoin, Polígono, Sui, Aptos, e Você. Associado ao coprocessador ZK de sub-segundo, os desenvolvedores podem construir aplicativos com dados de blockchain sem confiança e fornecer resultados de consulta por meio da integração da plataforma com Chainlink.
Design de Token
Com Espaço e Tempo, os desenvolvedores podem facilmente criar seus próprios tokens em minutos. Eles podem ditar, ajustar e otimizar as utilidades e o plano de distribuição do token, se preparar para os riscos de mercado potenciais para garantir estabilidade e preparar relatórios visuais claros e concisos sobre a tokenomia para investidores e membros da comunidade.
Ecossistema SXT Chain
A cadeia SXT está ligada a uma infinidade de projetos de diferentes aspectos da indústria. Ela atravessa DeFi, IA, jogos, redes sociais, infraestrutura, RWA e muito mais, levando a uma nova era de dApps no setor de blockchain.
Atualmente, ele suporta projetos como Mainnet Ethereum, Era ZKsync, Bitcoin, Sui, Aptos, e Polígono.
Casos de Uso do Espaço e do Tempo (SXT)
Space and Time (SXT) oferece aos desenvolvedores várias maneiras de construir e aprimorar seus produtos, criando mais possibilidades e fornecendo mais serviços aos usuários e ao ecossistema. Ao utilizar a plataforma Space and Time, os desenvolvedores têm acesso aos seguintes serviços:
Coprocessor ZK de Sub-segundo
Os desenvolvedores podem construir contratos inteligentes através da plataforma Space and Time que podem fazer perguntas orientadas por dados sobre dados armazenados de importantes fontes on-chain e off-chain. Isso permite que os desenvolvedores entreguem dados on-chain para seus contratos inteligentes dentro do tempo de bloco.
Desenvolvimento de aplicativos on-chain
Com Space and Time (SXT), os desenvolvedores podem implantar a interface do aplicativo e o contrato inteligente e, em seguida, delegar os outros processos à plataforma para cuidar. Os desenvolvedores podem construir aplicativos orientados a dados equipados com APIs SQL pré-construídas, implantar aplicativos sem gerenciar a infraestrutura do backend eles mesmos.
Space and Time (SXT) fornece aos desenvolvedores APIs Web3 pré-construídas que alimentam seus aplicativos com dados de blockchain em tempo real comprovados por ZK coletados de blockchains principais. Os desenvolvedores também podem mesclar seus dados de blockchain com seus dados de plataforma desenvolvidos por meio de uma única consulta.
Os desenvolvedores também podem publicar suas consultas em painéis personalizados e integrá-las em seus aplicativos. Por último, eles também podem construir modelos de ML/AI através de dados à prova de violação de dados de fontes fora da cadeia e dentro da cadeia.
DeFi/Empréstimos
Com Espaço e Tempo, os desenvolvedores podem mesclar as pontuações de crédito de usuários do mundo real com transações on-chain para construir um novo sistema de pontuação de crédito Web3 para plataformas de empréstimos descentralizadas.
Jogos e NFTs
Com Space and Time, os desenvolvedores podem criar aplicativos com jogabilidade aprimorada e otimizada ganhos on-chain. Isso é possível por meio de transações/atividades on-chain geradas no jogo e análises avançadas sobre o comportamento da comunidade, concedendo aos desenvolvedores mais informações sobre as atividades no jogo que levaram a transações on-chain.
Os desenvolvedores também podem potencializar seus jogos com transações rápidas, analisar rapidamente terabytes de dados, usar contratos inteligentes para consultar o Espaço e o Tempo diretamente e criar recompensas ganhas em eventos do jogo.
Notícias sobre Espaço e Tempo
Em 27 de agosto, a Space and Time Labs anunciou que havia garantido US$ 20 milhões em financiamento da Série A, elevando o financiamento total da plataforma para US$ 50 milhões. O financiamento foi obtido de investidores respeitáveis como Framework Ventures, Lightspeed Faction, Arrington Capital e Hivemind Capital.
Espaço e Tempo são um Bom Investimento?
Sendo um armazém de dados descentralizado Web3, Space and Time combina o melhor dos dados on-chain e off-chain, mudando a forma como os usuários, desenvolvedores e aplicativos descentralizados lidam com dados. Sua arquitetura única e a integração do Proof of SQL abrem as portas para muitos novos casos de uso da tecnologia blockchain.
Artigos Relacionados

O que é o Protocolo Morpho?

Como apostar ETH?

O que é o PolygonScan e como você pode usá-lo? (Atualização 2025)

O que é Bitcoin?

O que é Tronscan e como você pode usá-lo em 2025?


